Modeling marital and family behavior of the rural population: statistical and sociological analysis
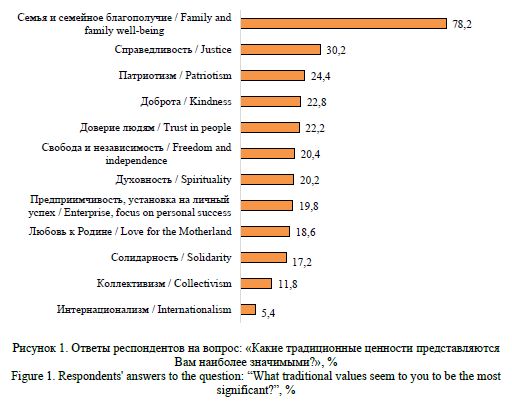
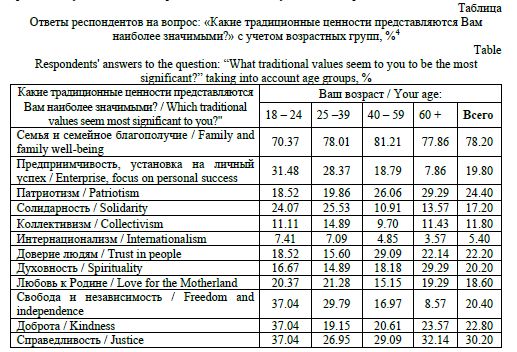
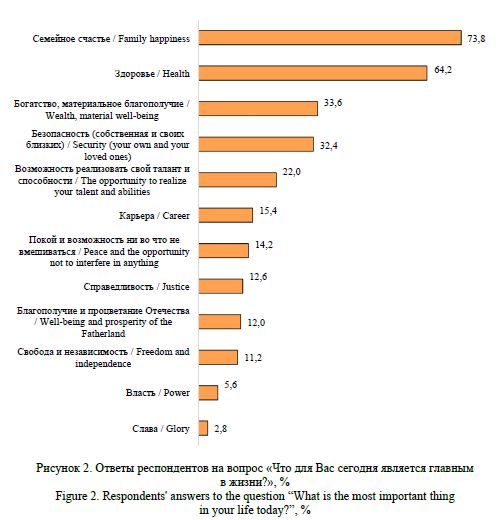
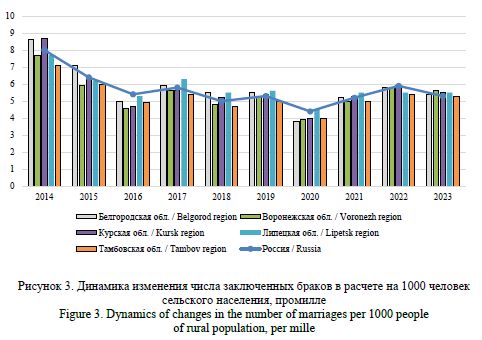
The relevance of the stated research problem is determined by the special role of marital and family behavior of the population in ensuring the socio-demographic security of rural areas. Acting as elements of a holistic model of demographic behavior, they determine not only the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of the demographic potential of rural areas, but also have a direct impact on the reproductive behavior of residents. Global social changes, increased population mobility, urbanization and cultural transformation processes have led to the weakening of the family as a social institution of society, a change in its place in value orientations. The scientific problem lies in the contradiction between significant changes in the models of marital and family behavior of rural communities in Russia, caused by their saturation with non-traditional elements that change the essential characteristics of the family as a social institution, and the lack of justification for the mechanisms and consequences of this process for the reproduction of rural areas and society as a whole. The formulation and prospects for solving the problem are associated with the need to empirically analyze and substantiate the key trends in changing marital and family behavior of the population of rural areas of the Central Black Earth Economic Region. For conceptualization in the work, general and specific methods of scientific research (analysis, synthesis, analogy, comparison, concretization, the method of formal-logical analysis, graphic, structural-functional methods), as well as statistical (summary and grouping of statistical observation materials, construction of dynamic series) and a set of sociological research methods (questionnaire survey, in-depth expert interview, focus groups) were used. Research Results. Understanding of specifics of population reproduction processes based on statistical research allows to draw a conclusion about significant transformation of model of matrimonial behavior of rural population caused by totality of social, economic, epidemiological and geopolitical factors of demographic reproduction. Application of sociological methods allowed to supplement the conducted analysis and substantiate main tendencies in change of marital and family behavior of rural residents. Conclusions. Crisis tendencies of demographic development and geopolitical tension, especially characteristic for border rural territories of Belgorod and Kursk regions, have significant influence on transformation of models of family and marital behavior of population. The conducted analysis shows the continuing leveling of the importance of the institution of family and marriage, the devaluation of family relations (according to statistical sources) while simultaneously declaring the high importance of the family as a traditional value (according to sociological research). This trend not only reduces the birth rate, but also prevents the younger generation from forming stable family values based on the experience of their parents, which will most likely lead to a deepening of the crisis in the demographic sphere of society in the future.
Figures
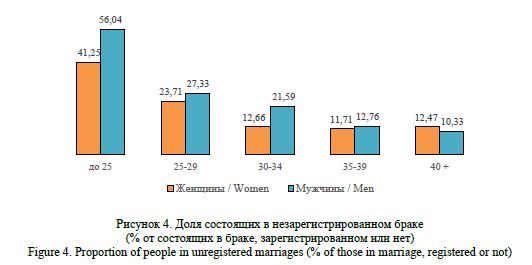
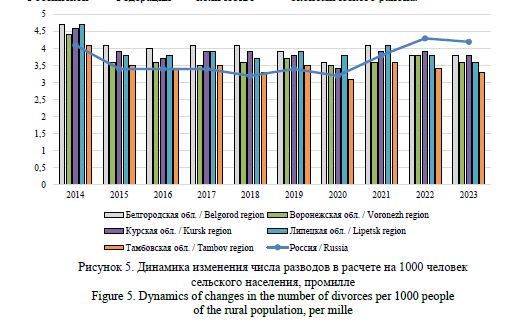
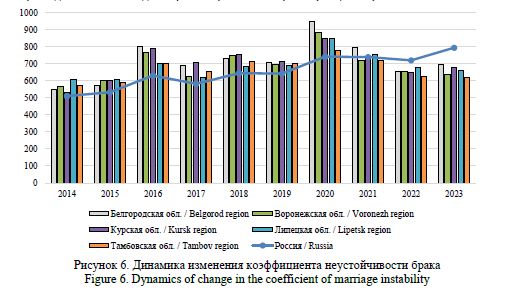
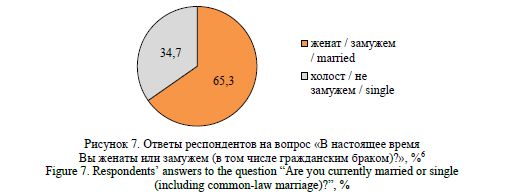
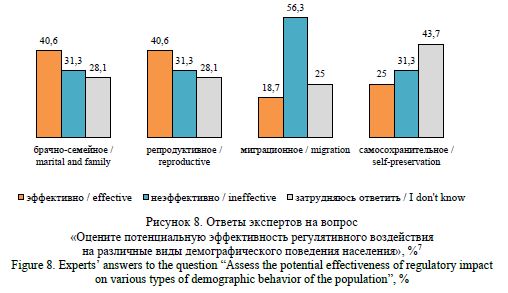
Gaidukova, G. N. (2024), “Modeling marital and family behavior of the rural population: statistical and sociological analysis”, Research Result. Sociology and Management, 10 (4), 226-244. DOI: 10.18413/2408-9338-2024-10-4-1-2


















While nobody left any comments to this publication.
You can be first.
Babintsev, V. P., Gaidukova, G. N & Shapoval, Zh. A. (2023), “Formation of the subjectivity of regional communities in Russia: a socio-cultural aspect”, Region: jekonomika i sociologija, 2(118), 121-143. (In Russian)
Blagorozheva, Zh. O. & Shapovalova, I. S. (2024), “The influence of alternative values and attitudes on the matrimonial strategies of youth”, Social'naja politika i sociologija, 23-2 (151), 30-39. (In Russian)
Vishnevskiy, A. G. (2014), “The demographic revolution is changing the reproductive strategy of the Homo sapiens species”, Demographic Review, 1 (1), 6-33. (In Russian)
Gurko, T. A. (2020), “Theoretical approaches to the study of the transformation of the family institution”, Sociologicheskij zhurnal, 26 (1), 31-54, DOI https://doi.org/10.19181/socjour.2020.26.1.7052. (In Russian)
Rostovskaya, T. K., Shabunova, A. A., Abdul`zyanov, A. R. (2024), Demograficheskoe samochuvstvie regionov Rossii: Nacional'nyj demograficheskij doklad – 2023 [Demographic well-being of the regions of Russia: National demographic report - 2023], Vologodskij nauchny`j centr, Vologda, Russia, DOI https://doi.org/10.19181/monogr:978-5-89697-427-7.2024. (In Russian)
Ippolitova, E. A. (2012), Semejnye perspektivy molodezhi v izmenjajushhemsja mire [Family Prospects for Youth in a Changing World], AZBUKA, Barnaul, Russia. (In Russian)
Kalachikova, O. N., & Gruzdeva, M. A. (2018), “Changes in the reproductive and marital behavior of the Russian population (based on the analysis of sample studies by Rosstat)”, Social Area, 2 (14), DOI: https://doi.org/10.15838/sa.2018.2.14.1. (In Russian)
Kobleva, Z. X. (2023), “Premarital cohabitation as a model of matrimonial behavior of young people”, Izvestija Jugo-Zapadnogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta. Serija: Jekonomika. Sociologija. Menedzhment, 13 (3) 220-230. DOI: 10.21869/2223-1552-2023-13-3-220-230. (In Russian)
Kovaleva, Yu. V. (2012), “Joint regulation of the behavior of spouses at various stages of the family life cycle”, Psihologicheskij zhurnal, 33(5), 50-70. (In Russian)
Noskova, A. V. (2015), “New methodological approaches, research focuses, debatable problems of family sociology”, Sociological Studies, 10 (378), 177-185. (In Russian)
Sementsova, K. R. (2022), “Marital and family behavior of young people in modern Russian society: attitudes and values”, Humanities and Social Sciences. Bulletin of the Financial University, 12 (4), 109-113. DOI: https://doi.org/10.26794/2226-7867-2022-12-4-109-113. (In Russian)
Sidorkina, V. M., & Fadeeva, I. M. (2017), “Family values in regional society: factors of change”, Russian Journal of Regional Studies, 25 (4), 628-641. (In Russian)
Toshhenko, Zh. T., & Velikij, P. P. (2018), “The main views on the life of rural residents of Russia”, Mir Rossii. Sociologija. Jetnologija, 27 (1), 7-33, DOI: https://doi.org/10.17323/1811-038X-2018-27-1-7-33. (In Russian)
Babintsev, V., Gaidukova, G., & Shapoval, Z. (2021), “On the problem of renovation of socio-cultural constants that have constructive potential for development of regional communities”, SHS Web of Conferences (IFSDR 2021), 128, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/shsconf/202112804003.
Cherlin, A. J. (2004), “The deinstitutionalization of American marriage”, Journal of Marriage and Family, 66(4), 848-861.
Fasang, A. E., Gruijters, R. J., & Van Winkle, Z. (2024), “The life course boat: A theoretical framework for analyzing variation in family lives across time, place, and social location”, Journal of Marriage and Family, 86 (5), 1586-1606. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jomf.13012.
Goldberg, A. E., & Allen, K. R. (2024), “Qualitative family research: Innovative, flexible, theoretical, reflexive”, Journal of Marriage and Family, 86 (5), 1323-1352, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jomf.12981.
England, P. (2010), “The gender revolution: Uneven and stalled”, Gender & Society, 24 (2), 149-166.
Hogendoorn, B., & van den Berg, L. (2024), “The educational diffusion of divorce: The role of gender and context”, Journal of Marriage and Family, 86 (3), 738-761, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jomf.12980.
Józefczyk, A. (2023), “Multigenerational transmission of differentiation of self-Toward a more in-depth understanding of Bowen's theory concept”, Journal of Marital and Family Therapy, 49, 634-653, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jmft.12645.
Longo, G. M. (2023), “The internet as a social institution: Rethinking concepts for family scholarship”, Family Relations, 72 (2), 621-636.
McErlean, K. (2024), “Cohabiting couple's economic organization and marriage patterns across social classes”, Journal of Marriage and Family, 86 (3), 762-786, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jomf.12947.
Madhavan, S. (2024), “Families on the space–time continuum: Conceptualizing and measuring temporal and spatial dimensions”, Journal of Marriage and Family, 86 (5), 1541-1556, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jomf.12984.
Morris, K.L., McDowell, C.N., Tawfiq, D., Outler, C., & Kimmes, J.G. (2024), “Relationship mindfulness, negative relationship quality, and physical health”, Journal of Marital and Family Therapy, 50, 136-149. DOI: 10.1111/jmft.12677.
Odasso, L., & Geoffrion, K. (2023), “Doing family online: (in)formal knowledge circulation, information-seeking practices, and support communities”, Family Relations, 72 (2), 389-405.
Perez, C., Fife, S. T., Eggleston, D., & Whiting, J. B. (2023), “Justifying by degrees: A grounded theory of men's decision-making process in infidelity”, Journal of Marital and Family Therapy, 49, 879-898, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jmft.12663.
Pesando, L. M. (2018), “Global family change: Persistent diversity with development”, Population and Development Review, (5), 133-168, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/padr.12209.
Qian, Y., & Hu, Y. (2024), “The digitalization of family life: A multilevel conceptual framework”, Journal of Marriage and Family, 86(5), 1160-1183, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jomf.12983.
Rostovskaya, T. K., Sitkovsky, A. M. (2024), “Demographic development resources: On the unification of concepts in demographic research”, Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast, 17 (1), 178-200, DOI: https://doi.org/10.15838/ esc.2024.1.91.10.
Ruggles, S. (2010), “Stem families and joint families in comparative historical perspective”, Population and Development Review, 36 (3), 563-577, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1728-4457.2010.00346.x.
Shabunova, A. A., Rostovskaya, T. K. (2020), “On the necessity to develop models of optimal conditions for the formation and implementation of demographic attitudes”, Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast, 13 (4), 38-57, DOI: https://doi.org/10.15838/esc.2020.4.70.2.
Therborn, G. (2014), “Family Systems of the World: Are they converging?”, The Wiley Blackwell companion to the sociology of families, in Treas, J., Scott, J. & Richards, M. (eds.), John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 1-19. DOI: https://doi.org/0.1002/9781118374085.ch1.
Vidal, S., & van Damme, M. (2024), “Women's family trajectories after union dissolution: A comparative life course analysis”, Journal of Marriage and Family, 86 (2), 369-390, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jomf.12972.